Can you tell the difference? Google.com vs. Goōgle.com
Posted in Announcements News
If you can’t tell the difference, your computer, your data, and your identity may be toast!
Site spoofing
It is exactly what it sounds like. Site spoofing allows one identical-looking domain to spoof another well-known or more legitimate domain. One old example was not exactly malicious, but it was not harmless. About 10 years ago, the site “whitehouse.com” was frequently confused with “whitehouse.gov” and navigated to a not-family-friendly page that wasn’t the official site of 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue. But the difference between .com and .gov is easy to spot and just takes a bit of careful typing to avoid browsing to the wrong site.
Today, the spoofing is much more elaborate and can result in serious damage to your computer, your personal information, and the network you’re connected to – whether at home or work. Using tactics like URL hijacking, brandjacking, and homograph attacks, internet hackers are out to lead you astray.
Here are some recent examples of hackers using punycode to impersonate legitimate websites to direct unsuspecting users to interact with malicious code and ransomware. Would you be able to spot the difference?
| Malicious site | Fake URL | How it can appear in your browser |
| torbrwser-zxb.com | torbrōwser.com | https://www.torbrowser.com |
| brav-eva.com | bravē.com | https://www.brave.com |
| flghtsimulator-mdc.com | flīghtsimulator.com. | https://www.flightsimulator.com |
| tlegram-w7a.com | tēlegram.com | https://www.telegram.com |
Does your browser have your back? Check for yourself
Open this perfectly safe (trust us, we’re on your side) URL in the web browser of your choice.
https://www.xn--80ak6aa92e.com
It’s a fake “apple.com” site. Does the browser you use know the difference?
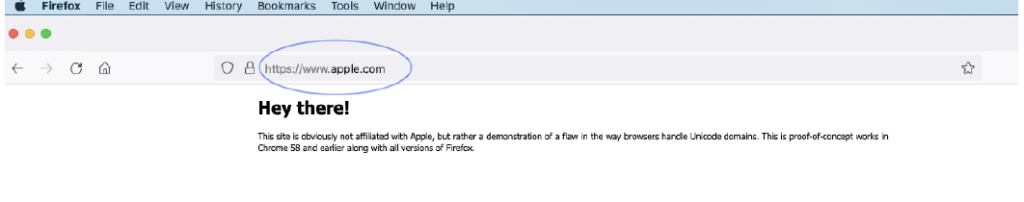
How Firefox treated the spoofed site: Appeared as a legitimate Apple site. 👎
Not Cool, Firefox.
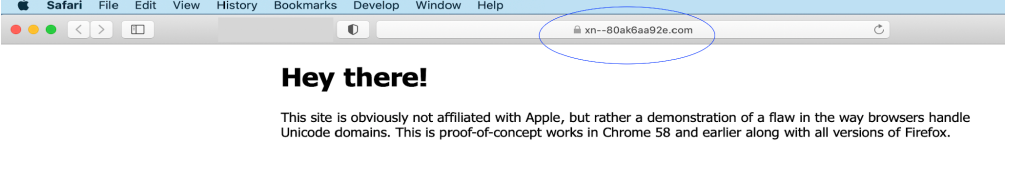
How Safari treated the spoofed site: Appeared as the actual fake domain.👍
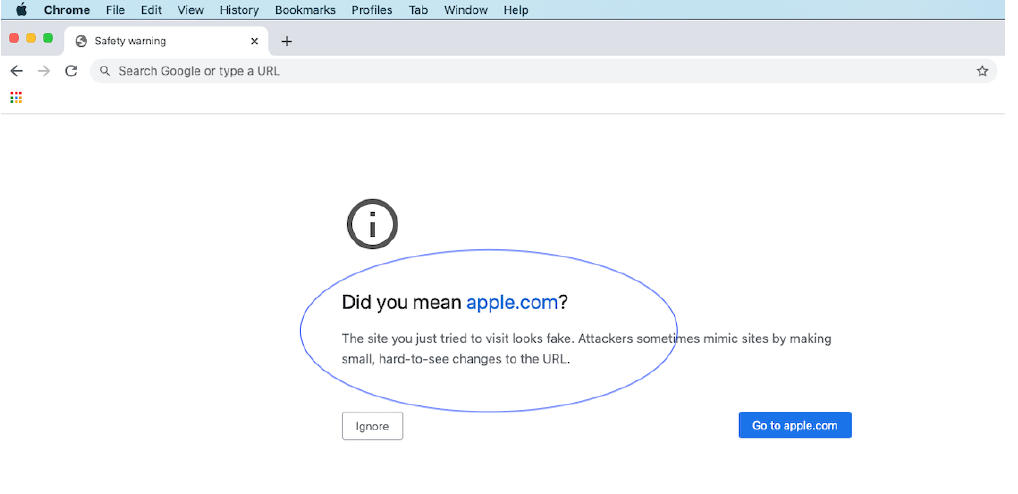
How Chrome treated the spoofed site: Warned users that the site is fake.👍
Phishing is not just in email
You can get caught by these scammers by clicking on legit-looking ads on websites, social media, and even Google itself. Through the use of clever proxies and layers, clicking on an ad for a trendy new water bottle can actually be the start of a ransomware download.

Figure 1 Beware the “download here” or “buy now” button if you got there via an advertisement or unverified site.
How you can protect yourself
While your web browser may offer some clues when you click a fake site, it’s not foolproof. Here are a few clear ways to avoid getting caught in these URL traps:
1. Always take a few extra seconds to inspect the URL as it appears in the address bar.
2. Wherever you can, avoid clicking on advertisements directly from Google or other sites. If you’re interested in a particular product or sale, try opening a new tab and typing the vendor or retailer name directly in your browser window.
3. Always visit websites from your own bookmarks or by typing the URL, never from a link in an unverified email or page.
4. Use a web browser that helps you identify the fakes. (For example: Google Chrome and Apple Safari)
